steam cell therapy
Stem Cell Therapy is an innovative and regenerative medical treatment that utilizes stem cells to repair, regenerate, and heal damaged tissues in the body. It has shown great promise in treating various musculoskeletal, joint, and degenerative conditions. The therapy involves harnessing the body’s own healing properties to promote tissue recovery without the need for invasive surgery.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Work?
Stem cells are unique because they have the ability to transform into various types of cells, including cartilage, muscle, bone, and nerve cells. They can repair tissues by multiplying and regenerating damaged areas.
In stem cell therapy, stem cells are usually harvested from the patient’s own bone marrow or fat tissue, processed, and then injected into the damaged or affected area (such as joints, tendons, or ligaments). The stem cells then stimulate healing, reduce inflammation, and help restore function to the injured tissue.
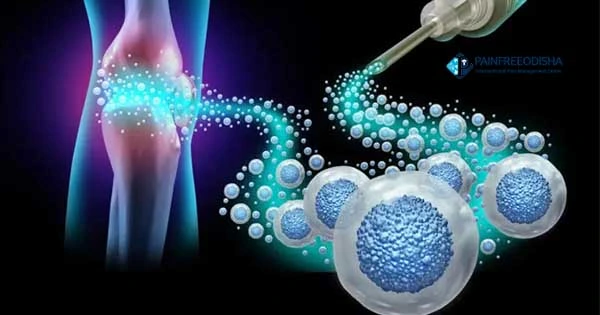

Conditions Treated by Stem Cell Therapy
Osteoarthritis (OA)
✔ Knee Osteoarthritis – Regenerates cartilage and reduces joint pain. ✔ Hip & Shoulder Osteoarthritis – Improves joint mobility and delays the need for joint replacement. ✔ Spinal Osteoarthritis – Treats degenerative changes in spinal discs.

Cartilage Damage & Degeneration
✔ Meniscus Tears – Helps repair damaged cartilage in the knee. ✔ Chondromalacia Patella – Promotes healing of the soft cartilage under the kneecap. ✔ Joint Surface Damage – Regenerates articular cartilage in damaged joints.

Ligament & Tendon Injuries
✔ ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) Tears – Stimulates the healing of torn ligaments in the knee. ✔ Rotator Cuff Injuries – Promotes healing of torn tendons in the shoulder. ✔ Achilles Tendonitis – Helps repair damage to the Achilles tendon. ✔ Elbow Tendonitis (Tennis & Golfer’s Elbow) – Reduces inflammation and promotes tendon regeneration.
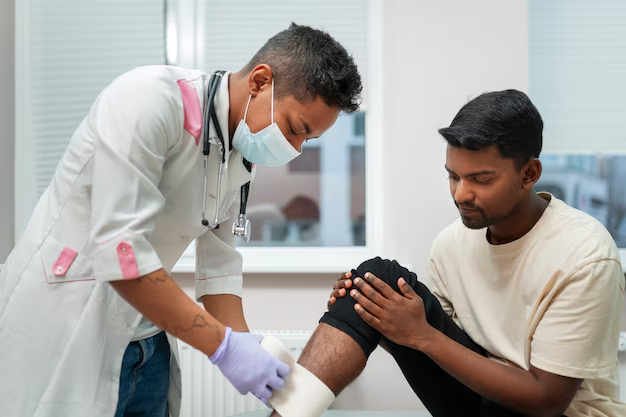
Sports Injuries
✔ Sprains & Strains – Stimulates healing of soft tissue injuries. ✔ Stress Fractures – Speeds up healing and reduces recovery time. ✔ Joint Instability – Helps stabilize weakened joints due to sports-related trauma.

Sports Injuries
✔ Sprains & Strains – Stimulates healing of soft tissue injuries. ✔ Stress Fractures – Speeds up healing and reduces recovery time. ✔ Joint Instability – Helps stabilize weakened joints due to sports-related trauma.

Chronic Pain Conditions
✔ Chronic Back Pain – Alleviates pain caused by degenerative discs or joints. ✔ Chronic Neck Pain – Reduces pain from spinal injuries or degenerative conditions. ✔ Hip Pain – Eases long-term pain from hip joint degeneration. ✔ Joint Inflammation – Reduces inflammation in joints affected by arthritis or injuries.

Bone Injuries & Healing Issues
✔ Non-Union Fractures – Promotes bone regeneration in fractures that fail to heal. ✔ Delayed Healing Fractures – Helps accelerate the healing process. ✔ Osteonecrosis (Bone Death) – Stimulates repair in bones affected by reduced blood flow.

Autoimmune & Inflammatory Conditions
✔ Rheumatoid Arthritis – Helps reduce inflammation and pain in affected joints. ✔ Psoriatic Arthritis – Provides relief from joint pain and swelling. ✔ Lupus – May be used to treat systemic inflammation and joint pain.

Soft Tissue Injuries
✔ Tendon Tears – Stimulates healing of torn or damaged tendons. ✔ Ligament Sprains – Promotes healing of stretched or torn ligaments. ✔ Muscle Strains – Helps regenerate damaged muscle tissues.

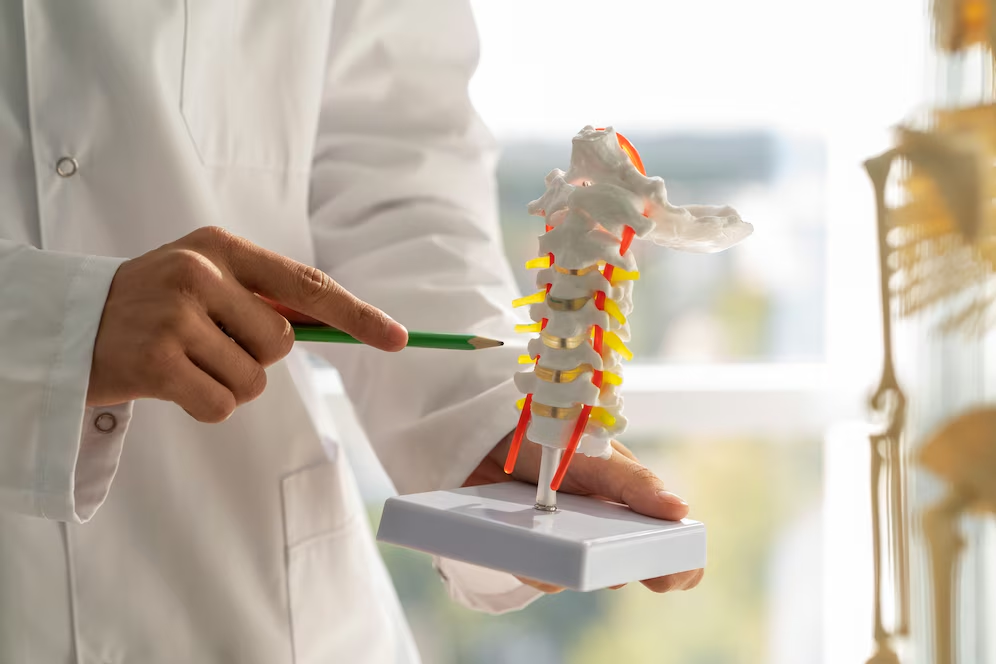
Spinal Conditions
✔ Degenerative Disc Disease – Regenerates spinal discs to improve flexibility and reduce pain. ✔ Herniated Discs – Helps repair damaged discs and reduce nerve compression. ✔ Spinal Stenosis – Reduces inflammation and improves spinal mobility.

Stem Cell Therapy Procedure
Step 1: Initial Consultation
🔹 The patient undergoes a comprehensive evaluation by a physician who specializes in stem cell therapy.
🔹 Medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests (such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound) are used to determine the extent of the damage and if stem cell therapy is appropriate.
Step 2: Stem Cell Harvesting
🔹 Bone Marrow or Fat Tissue Collection – Depending on the type of stem cells being used, stem cells are typically extracted from two main sources:
- Bone Marrow: Harvested from the hip bone (iliac crest).
- Adipose (Fat) Tissue: Extracted from areas like the abdomen or thighs using a minimally invasive method.
🔹 Local anesthesia is used to numb the area where the stem cells will be extracted. The procedure is generally quick and minimally painful.
🔹 A specialized needle is inserted into the bone or fat to extract the stem cells, which takes about 15-30 minutes.
Step 3: Stem Cell Processing & Concentration
🔹 The harvested bone marrow or fat tissue is placed in a centrifuge, a machine that spins at high speeds to separate the stem cells and growth factors from other cells.
🔹 The concentrated stem cells, along with platelets and growth factors, are now ready for injection into the damaged tissue or joint.
🔹 This process usually takes about 30-45 minutes.
Step 4: Injection of Stem Cells
🔹 Using ultrasound guidance or fluoroscopic imaging, the physician carefully injects the concentrated stem cell mixture directly into the damaged joint or area of injury (e.g., knee, shoulder, or spine).
🔹 The injection is typically done in an outpatient setting, and patients may experience some mild discomfort during or after the procedure.
🔹 This step generally takes around 15-30 minutes, depending on the number of injection sites.
Step 5: Post-Procedure Care
🔹 After the procedure, patients are monitored for a short period (about 30-60 minutes) to ensure there are no immediate complications.
🔹 Mild swelling, soreness, or bruising at the injection site may occur, but it usually subsides within a few days.
🔹 Patients are advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities for 48-72 hours following the procedure.
Step 6: Follow-Up & Rehabilitation
🔹 Patients typically begin to see improvements in pain and mobility within 2-6 weeks, with optimal results often occurring in 3-6 months.
🔹 A rehabilitation program such as physical therapy may be recommended to help strengthen the affected area and improve range of motion.
🔹 Regular follow-ups with the treating physician help monitor progress and determine if additional treatments are needed.
